
This can appear to show EPS growth, even while earnings may be static or declining. EPS is affected by a company’s earnings and number of outstanding shares. If earnings decrease or the number of shares increases, EPS will decline as well. Earnings forecasts are based on educated guesswork from analysts and are often too rosy, possibly making the valuation look cheap.
How to Find Earnings Per Share on Income Statement?
But investors may be willing to pay a higher P/E ratio for a smaller, faster-growing company than a slow-growing or stagnant company. The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site.
What is adjusted EPS?
The day trading world responded enthusiastically to this major beat, and the stock closed more than 21% higher the next day. If a company’s most recent quarterly EPS is $0.12, and its EPS in the same quarter last year was $0.09, then it has a quarterly year-over-year EPS growth rate of 33%. Quarterly year-over-year EPS growth is a company’s most recent quarterly EPS divided by its EPS from the same quarter the prior year, minus 1. Annual EPS growth is a company’s EPS over the last year divided by its EPS over the prior year, minus 1. EPS growth is pretty self-explanatory; it’s a way of measuring how fast a company is growing in terms of its earnings. In some cases, companies may also provide an adjusted EPS number, which is usually diluted EPS with atypical one-time items removed.
- Understanding how to find EPS is crucial for evaluating a company’s profitability.
- The amount earned by each share of common stock is represented as basic earnings per share in the company income statement.
- As with any fundamental metric, earnings per share on its own doesn’t define whether a stock is a buy or sell.
- Investors can compare the EPS of Bank of America with other financial institutions, such as JP Morgan Chase (JPM) or Wells Fargo (WFC), to get an idea of relative financial strength.
Forward EPS
Adjusted EPS is a type of EPS calculation in which the analyst makes adjustments to the numerator. Typically, this consists of adding or removing components of net income that are deemed to be non-recurring. However, assume that this company closed 100 stores over that period and ended the year with 400 stores. An analyst will want to know what the EPS was for just the 400 stores the company plans to continue with into the next period. The higher a company’s EPS, the more profitable it is considered to be. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
Rolling EPS vs. Trailing EPS
The P/E ratio is used to analyze a stock’s value, while EPS is used to determine a stock’s profitability. Instead, you could look at the EPS trend over time to see if the company is on its way to becoming profitable, or evaluate other metrics like revenue growth, customer acquisition, book value, etc. Quarterly income statements can be accessed from the company’s 10-Q filings on either the SEC or company website, where they’re usually in the investor relations section.
If a company misses or beats analysts’ consensus expectations for EPS, its shares can either crash or rally, respectively. Diluted EPS, on the other hand, will always be equal to or lower than basic EPS because it includes a more expansive definition of the company’s shares outstanding. Specifically, it incorporates shares that are not currently outstanding but could become outstanding if stock options and other convertible securities were to be exercised.
Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range, can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range of offers, Bankrate does not include compensation information about every financial or credit product or service. Management teams often tout adjusted EPS as a better estimate of the company’s core performance. That may be the case sometimes, but when “one-time” losses recur quarter after quarter, smart investors begin to take the adjusted EPS figures with more than a grain of salt. The calculation of EPS relies on net income, which includes non-cash expenses such as depreciation and amortization, which are non-cash expenses.
If the two EPS measures are increasingly different, it may show that there is a high potential for current common shareholders to be diluted in the future. Companies with a complex capital structure must report both basic EPS and diluted EPS to provide a more accurate picture of their earnings. The main difference between basic EPS and diluted EPS is that the latter factors in the assumption that all convertible securities will be exercised. As such, basic EPS will always be the higher of the two since the denominator will always be bigger for the diluted EPS calculation. Earning per share is the same as any profitability or market prospect ratio.
As an investor, it is important to be aware of these practices and to understand a company’s financial statements in order to get an accurate picture of its profitability. This is commonly used by investors because it gives a more accurate picture of a company’s true profitability. To calculate basic earnings per share, diluted earnings per share is used in firms with a complicated financial structure.
In that event, the higher diluted share count is making the business look better than it might otherwise be. The accounting rules applied to diluted shares aim to prevent that outcome. As a result, investors and analysts often use EPS to evaluate stocks, as well as future EPS estimates to predict stock movements. The earnings per share (EPS) is a valuable measure of profit allocation across a company.
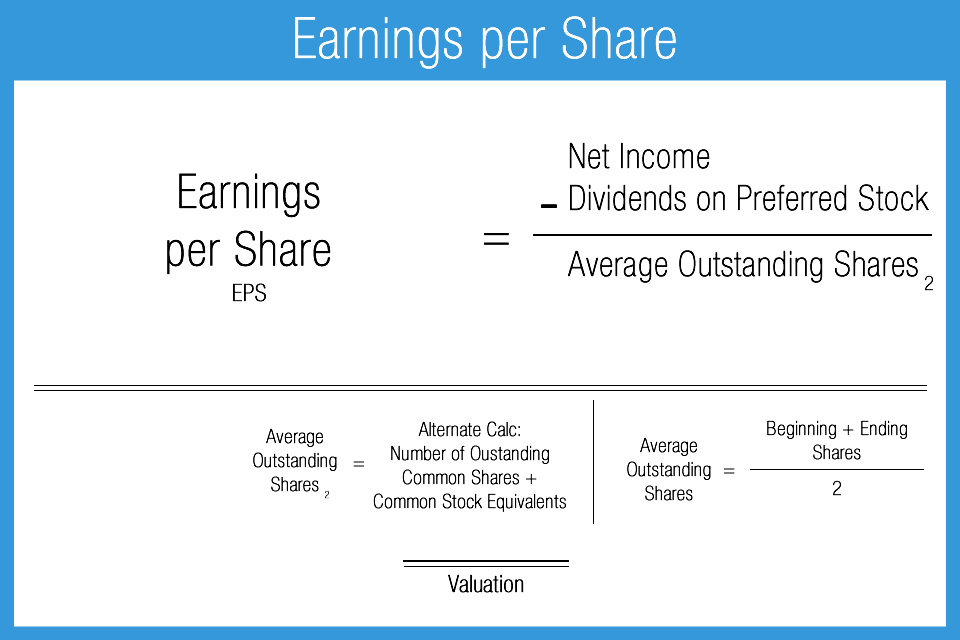
We now have the necessary inputs to calculate the basic EPS, so we’ll divide the net earnings for common equity by the weighted average shares outstanding. The earnings per share (EPS) reported by a company per GAAP accounting standards can be found near the bottom of a company’s income statement, right below net income. The Earnings Per Share (EPS) is the ratio between the net profit generated by a company and the total number of common shares outstanding. Basic EPS includes all of the company’s outstanding shares, while diluted EPS includes shares, stock options, warrants, and restricted stock units.